资源存档#
本次实验使用的课程代码版本为 CS144 Winter 2024,鉴于 CS144 官方要求禁止公开代码以防止抄袭,我将我的题解和原始代码存档放在了 Gitee 上(外国学生应该不知道这个平台吧),有需要可自取:CS144: CSS144 Winter 2024 Labs.。另外,我还托管了课程主页的镜像,各个资源链接如下:
虚拟机镜像#
CS144 官网给出了 Virtual Box 镜像及相应配置过程:Setting up your CS144 VM using VirtualBox。
Lab 0#
环境配置#
我使用的是 Ubuntu 22.04 @ WSL2,原文档给出了一个环境配置命令:
1
|
sudo apt update && sudo apt install git cmake gdb build-essential clang clang-tidy clang-format gcc-doc pkg-config glibc-doc tcpdump tshark
|
文档中提到测试环境是 Ubuntu 23.10 LTS+g++ 13.2,而上述命令并不能安装对应版本的 gcc,可以参考这篇文章安装最新的 g++:安装并切换指定gcc或者g++版本,在 Ubuntu 22 上最新只能安装 13.1 版本的 g++。后续实验均在此基础上进行。
现代 C++#
实验要求使用现代 C++ 风格进行编程,基本理念是:每个对象都只设计尽可能少的公共接口、内部存在各种安全检查、使用结束后应该正确回收垃圾,避免使用成对的关键字(例如 new 和 delete)。相反,通过构造函数和析构函数来获取和释放资源,即基于“资源获取即初始化”RAII 理念。
具体来说,对于编码风格有以下要求:
- 在编码过程中参考文档 cppreference.com
- 不要使用
malloc、free、new 或者 delete 关键字
- 不要使用原始指针,使用智能指针
- 不要使用模板、线程、锁或者虚函数
- 不要使用
C 风格字符串 char* 或者相关函数 strlen() 等
- 不要使用
C 风格类型转换,使用 C++ 的 static_cast 进行转换
- 函数形参尽可能使用
const 关键字
- 变量和函数都尽可能使用
const 关键字修饰
- 避免使用全局变量,每个变量的作用域都应该尽可能小
- 在提交前,使用
cmake --build build --target tidy 获取关于代码风格修改的建议,使用 cmake --build build --target format 对代码进行格式化。
Writing webget#
忽略前面通过 telnet 刚问网页和发送邮件的内容,第一个编码任务是完成 Webget,使之能够获取网页。这个任务比较简单,涉及到一点网络编程的知识。
整个任务的流程是:根据形参获取初始化主机地址,建立与该主机的 TCP 连接,发送 HTTP 请求报文(包含形参中的资源路径),打印响应报文,关闭 TCP 连接。
实现的代码为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
void get_URL( const string& host, const string& path )
{
Address addr = Address(host, "http");
TCPSocket sock = TCPSocket();
sock.connect(addr);
string message = "GET " + path +" HTTP/1.1\r\n" + "Host: "+host + "\r\n" +"Connection: close\r\n\r\n";
sock.write(message);
while(!sock.eof()){
string response;
sock.read(response);
cout << response;
}
sock.close();
cerr << "Function called: get_URL(" << host << ", " << path << ")\n";
cerr << "Warning: get_URL() has not been implemented yet.\n";
}
|
An in-memory reliable byte stream#
第二个任务是实现可靠的内存字节流,有以下几个要求:
- 输出端和输入端数据顺序一致,以 EOF 结尾
- 流量控制,即该字节流存在一个容量上限
- 容量上限指的是字节流中存在的数据的上限,而非发送者发送的字节流的上限。显然,我在实现时直接截断了超过剩余容量的输入
- 单线程使用,不需要考虑并发读写
任务要求实现如下接口:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
class Writer : public ByteStream
{
public:
void push( std::string data ); // Push data to stream, but only as much as available capacity allows.
void close(); // Signal that the stream has reached its ending. Nothing more will be written.
bool is_closed() const; // Has the stream been closed?
uint64_t available_capacity() const; // How many bytes can be pushed to the stream right now?
uint64_t bytes_pushed() const; // Total number of bytes cumulatively pushed to the stream
};
class Reader : public ByteStream
{
public:
std::string_view peek() const; // Peek at the next bytes in the buffer
void pop( uint64_t len ); // Remove `len` bytes from the buffer
bool is_finished() const; // Is the stream finished (closed and fully popped)?
uint64_t bytes_buffered() const; // Number of bytes currently buffered (pushed and not popped)
uint64_t bytes_popped() const; // Total number of bytes cumulatively popped from stream
};
|
为了记录累计读写量、维护剩余容量和端口是否关闭,在 ByteStream 添加了如下成员变量(别忘了在构造函数中初始化):
1
2
3
4
5
|
std::queue<char> buffer_; // 缓冲区
uint64_t amount_; // 剩余容量
uint64_t total_pushed_; // 总写入量
uint64_t total_poped_; // 总读取量
bool close_; // 端口状态
|
具体实现比较简单,维护一个队列 vector<string> 进行读写操作。在 Writer::push 的实现中,如果待写入数据超过了缓冲区剩余容量,则直接截断即可。指的注意的是 pop 采用了一种“lazy pop”的机制,即每次 pop 一个字节时,不要直接删除队头字符串的第一个字符,而是使用一个变量记录对头字符串还剩多少字节没有被 pop。
byte_stream.cc 的实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
|
#include "byte_stream.hh"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
ByteStream::ByteStream( uint64_t capacity ) :
capacity_( capacity ), buffer_(), amount_(0), total_pushed_(0),
total_poped_(0), first_string_left_size(0), close_( false ), error_( false ) {}
bool Writer::is_closed() const
{
// Your code here.
return close_;
}
void Writer::push( string data )
{
// Your code here.
uint64_t free_capacity = available_capacity();
uint64_t to_push_size = min(free_capacity, data.size());
if(to_push_size == 0) return;
data.resize(to_push_size);
buffer_.emplace(std::move(data));
if(buffer_.size() == 1)
first_string_left_size = to_push_size;
total_pushed_ += to_push_size;
amount_ += to_push_size;
return;
}
void Writer::close()
{
// Your code here.
close_ = true;
}
uint64_t Writer::available_capacity() const
{
// Your code here.
return capacity_ - amount_;
}
uint64_t Writer::bytes_pushed() const
{
// Your code here.
return total_pushed_;
}
bool Reader::is_finished() const
{
// Your code here.
return amount_ == 0 && close_;
}
uint64_t Reader::bytes_popped() const
{
// Your code here.
return total_poped_;
}
string_view Reader::peek() const
{
// Your code here.
if(amount_ == 0 || buffer_.empty()){
return string_view{};
}
const string& front = buffer_.front();
// return string_view(front.data()+front.size()-first_string_left_size,1);
// return string_view(&front[front.size()-first_string_left_size]);
return string_view(front).substr(front.size()-first_string_left_size);
}
void Reader::pop( uint64_t len )
{
// Your code here.
total_poped_ += len;
amount_ -= len;
while(len){
if(len >= first_string_left_size){
len -= first_string_left_size;
buffer_.pop();
first_string_left_size = buffer_.front().size();
} else{
first_string_left_size -= len;
len = 0;
}
}
}
uint64_t Reader::bytes_buffered() const
{
// Your code here.
return amount_;
}
|
最终吞吐量最高跑到了 34 Gbit/s。
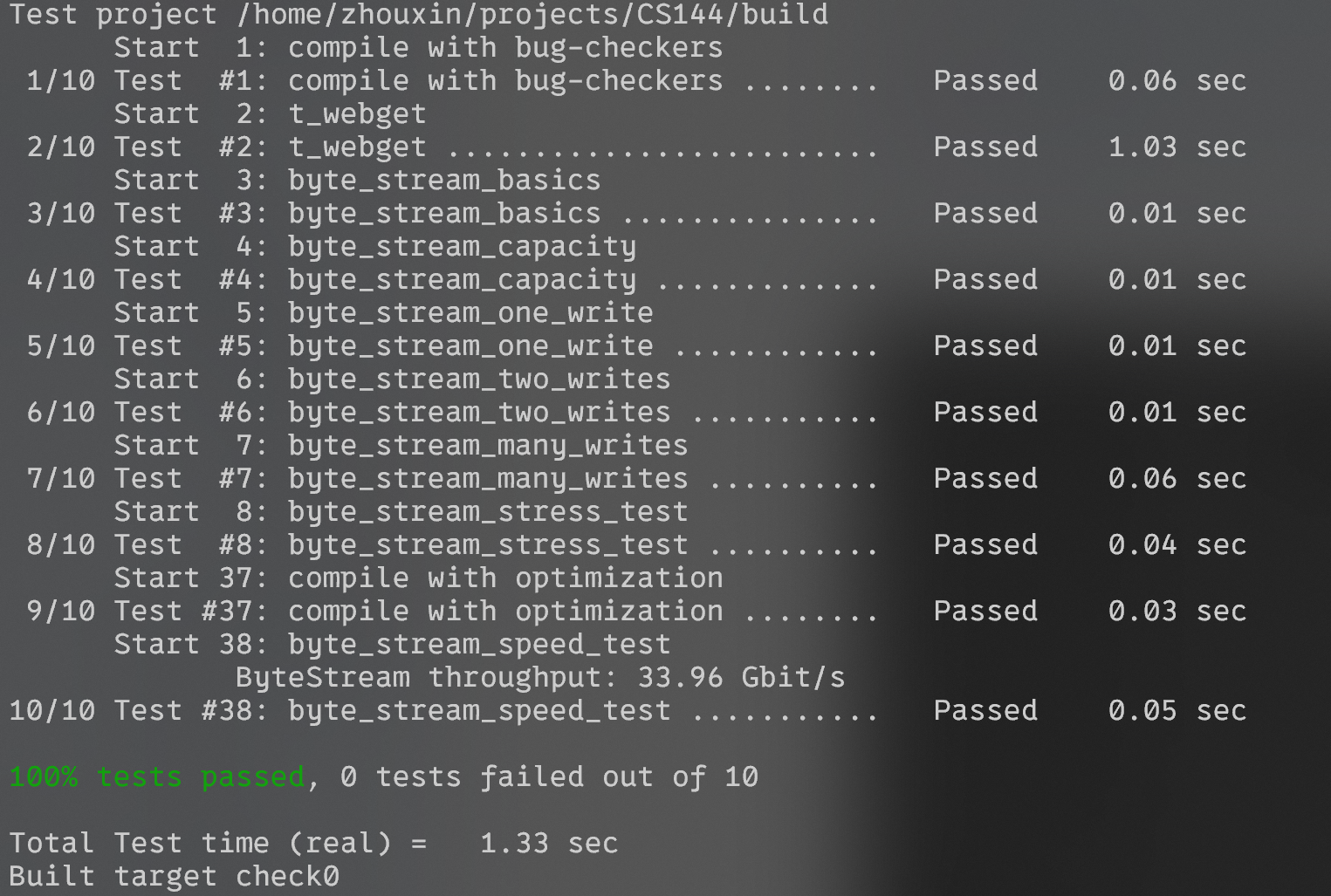
Lab 1#
Putting substrings in sequence#
这个模块要求实现一个 TCP 包重组模块,我感觉就是实现计网中 GBN 算法中的接受窗口,缓存收到的处于接收窗口内的 TCP 包、对其按序重组,并及时写入 Lab 0 中实现的可靠内存字节流中。做下来发现这个任务有以下几个要求:
- 实现包重组,包括乱序、重复、过期、截断等
- 该模块缓冲区不得大于内存字节流中的可用缓冲区大小
每个包到达时,有三个字段标识数据内容 data、包序号 first_index 和是否为最后一个包 is_last_substring,对于乱序到达的数据报,我们要暂存这些信息,我使用如下一个结构体保存每一个数据报:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
struct reassembler_item{
std::string data;
uint64_t first_index;
uint64_t last_index; // 左闭右开
bool is_last;
bool operator < (const reassembler_item& x) const{
return first_index < x.first_index;
}
reassembler_item(std::string data1, uint64_t first_index1, uint64_t last_index1, bool is_last1)
: data(std::move(data1)),
first_index(first_index1),
last_index(last_index1),
is_last(is_last1) {}
};
|
为了方便比较,我引入了一个字段用于表示这个包的数据表示的序号范围,采用左闭右开区间是因为存在一些空串(用来标识数据已经发送结束),其右闭区间为 -1,对于无符号数下溢了。
使用 vector 暂存收到的乱序数据报,并维护保证其始终有序且不存在重复元素。具体来说,在每次插入数据报时,使用 std::lower_bound 二分查找其待插入位置。找到插入位置后,待插入数据报可能向后覆盖了好几个已收到的数据报(例如,新收到的数据范围为 100~200,但是 110~120、190~210 范围的数据报在此之间已经收到并且保存在本模块缓冲区中),因此检查待插入位置后面可能被覆盖的元素,被待插入数据报完全覆盖的数据报直接扔掉,不完全覆盖的数据报则先拼接到待插入的数据报中,然后再扔掉。同样地,待插入数据报也有可能被待插入位置前的数据报覆盖,如果被完全覆盖了,则直接扔掉待插入数据报;如果被不完全覆盖,则拼接到前一个数据报后再扔掉。只有没被覆盖的数据报才需要被单独插入到模块内部暂存区中。
注意,上文所说的覆盖包含无重叠但相邻的情况,即 [1,200) 和 [200,300) 这两个数据包也是可以合并的。这可以保证如果有字符串可以向内存缓冲区写入,则这个字符串一定是且仅是暂存区的第一个数据包。
只有当暂存区新插入数据包时,才需要检查暂存区数据能否写入内存缓冲区。暂存区 insert 方法实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
|
void Reassembler::insert( uint64_t first_index, string data, bool is_last_substring )
{
// Your code here.
uint64_t capacity = output_.writer().available_capacity();
// 可以接受的序号范围为[current_index, current_index+capacity) 左闭右开
// data中数据的序号范围为[first_index, first_index+data.size())
// 二者取交集,若为空说明该串过期或者太早到来
uint64_t left_bound = max(first_index, current_index_);
uint64_t right_bound = min(current_index_+capacity, first_index+data.size());
if(right_bound < left_bound) { // 相等为空串,也能接受(可能标志了last_string)
return; // 对于buffer_没有更新操作,后续不会向缓冲区写入
}
reassembler_item item = reassembler_item(
data.substr( left_bound-first_index, right_bound-left_bound),
left_bound, right_bound, is_last_substring && right_bound == first_index+data.size());
pending_size_ += item.data.size(); // 先全部加进去,后面根据覆盖的内容再移除
auto insert_iter = lower_bound(buffer_.begin(), buffer_.end(), item);
// 先判断item是否向后覆盖了其它已插入buffer_的数据,如果有则合并
auto iter = insert_iter;
while (iter != buffer_.end() && item.last_index >= iter->first_index ){
if(item.last_index < iter->last_index) { // 只有部分覆盖才要合并,全覆盖直接erase即可
item.data += iter->data.substr(item.last_index-iter->first_index);
// 覆盖长度为item_last-iter_first
pending_size_ -= item.last_index - iter->first_index;
item.last_index = iter->last_index;
item.is_last |= iter->is_last;
}
else {
pending_size_ -= iter->data.size();
}
iter = buffer_.erase(iter);
}
// 再判断前一个数据是否覆盖了item
// 被前一个覆盖直接在前一个元素中修改,而不需要再插入item了
if(insert_iter != buffer_.begin()){
iter = insert_iter - 1;
if(iter->last_index >= item.first_index){
if(iter->last_index < item.last_index){ // 非完全覆盖
iter->data += item.data.substr(iter->last_index-item.first_index);
pending_size_ -= iter->last_index - item.first_index;
iter->last_index = item.last_index;
iter->is_last |= item.is_last;
} else { // 完全覆盖
pending_size_ -= item.data.size();
}
// 没插入,不需要删除的代码
// 直接return,不要运行后面插入insert代码
return;
}
}
// insert item into buffer_
buffer_.insert(insert_iter, item);
// 只有插入了新的item,才有可能需要向缓冲区写入
if(buffer_[0].first_index == current_index_){
auto& to_write_item = buffer_[0];
output_.writer().push(to_write_item.data);
pending_size_ -= to_write_item.data.size();
current_index_ = to_write_item.last_index;
if(to_write_item.is_last){
output_.writer().close();
}
buffer_.erase(buffer_.begin());
}
}
|
最终重组模块吞吐量最高跑到了 10 Gbit/s。
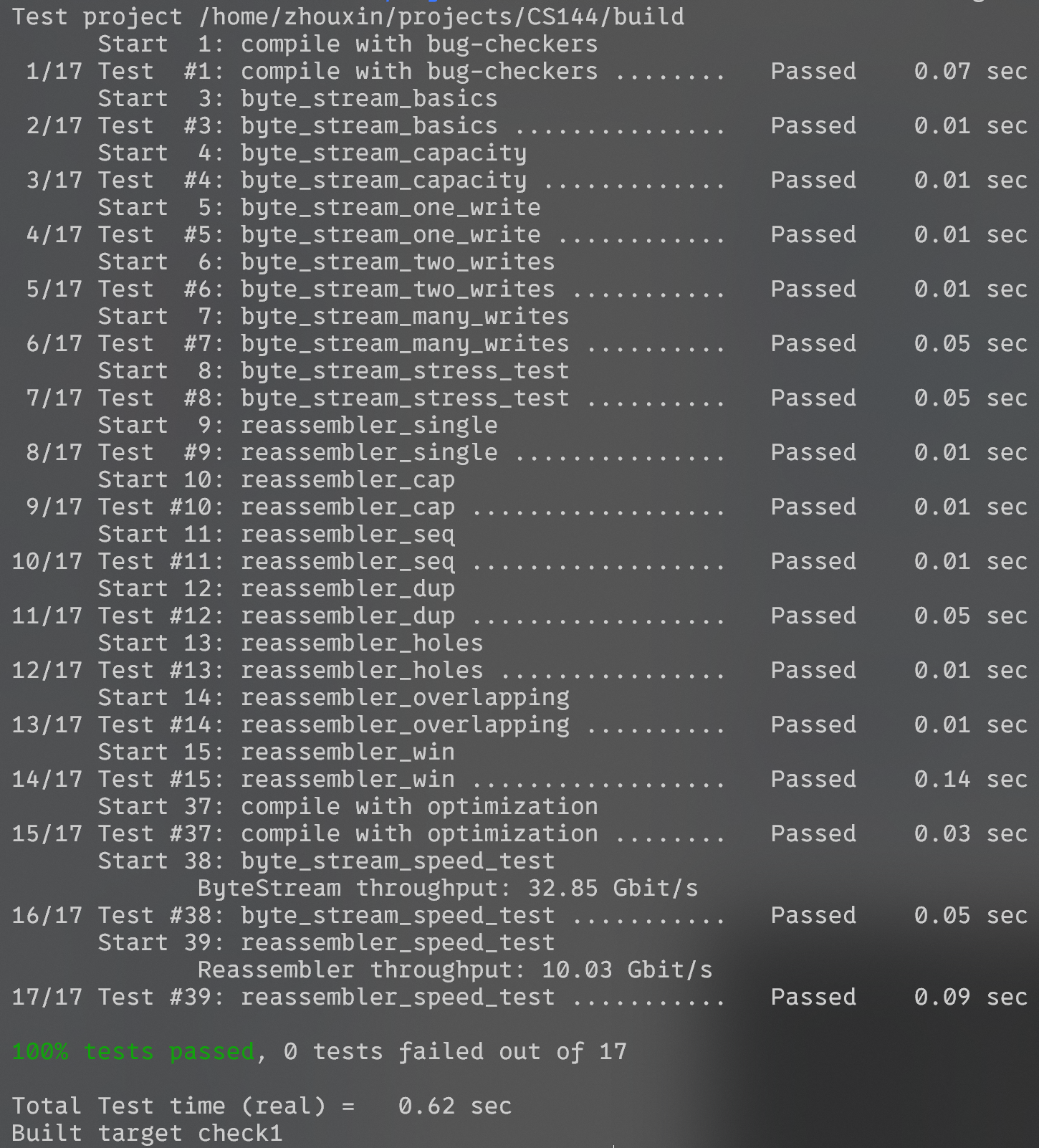
Lab 2#
到此为止,我们已经完成了内存可靠字节流和 TCP 包重组模块,重组模块将收到的 TCP 包进行重组,并及时写入内存字节流。接下来,我们需要写一个 TCP 接收器模块,接收来自 peer 发送方的消息,并回复 ACK 和接收窗口大小。
在此之前,有一个数据格式问题:在前两个模块中,我们使用 uint64 来标记序列号,可是在 TCP 的数据包只有 32 位用于记录序号,并且初始包(SYN)的序号可能是随机的。因此,我们首先要实现一个 32 位 TCP 包序号和 64 位绝对序号互相转换的模块。前者开始序号随机,并不断自增取余;后者固定从 0 开始自增,且我们认为总数据量不可能超过 2^64Byte,即 2^34GB。
Translating between 64-bit indexes and 32-bit seqnos#
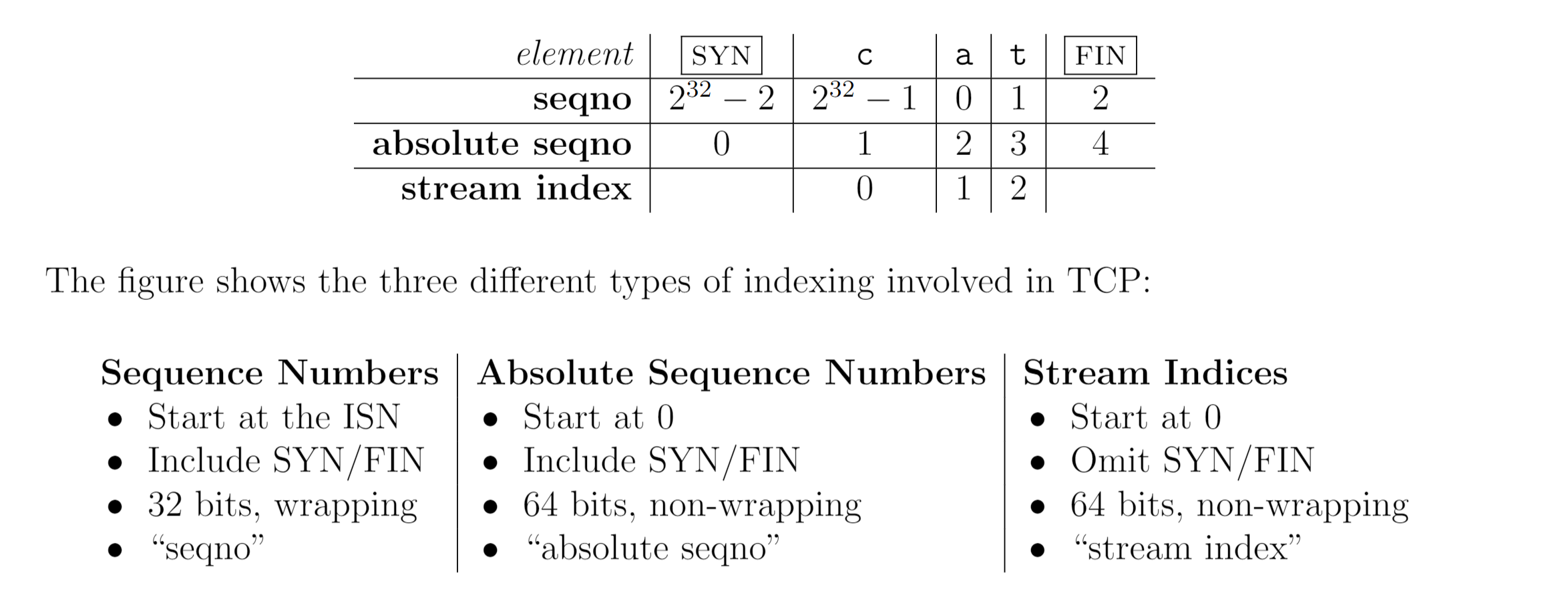
根据上图定义,不难发现 seqno 和 abs seqno 存在如下对应关系:
$$
seqno = (absSeqno+zeroPoint) % 2^{32}
$$
从 64 位转 32 位根据上式转换即可,其中对 2^32 取余是不必要的,因为 32 位数自动截断高 32 位。
从 32 位向 64 位转换,我们需要分开考虑其高低 32 位。首先是低 32 位,低 32 位标识了这个包的是整个序列的第 $absSeq%2^{32}$ 个包。那怎么通过 $seqno$ 计算它是整个序列的第几个包呢?$seqno$ 在自增过程中会不断取余,若不取余,记其为 $seqno’$,那么这个包是整个序列的第 $seqno’-zeroPoint$ 个包,而 $seqno’=seqno+n\times 2^{32}$,即:
$$
absSeq % 2^{32} = (seqno’-zeroPoint)%2^{32}
= (seqno+n\times 2^{32} - zeroPoint)%2^{32}
= (seqno-zeroPoint + 2^{32}) % 2^{32}
$$
上式即为计算绝对序号低 32 位的方法。得到低 32 位后,就要根据 checkPoint 得到高 32 位。显然,为了接近 checkPoint,高 32 位也是越接近越好,因此高 32 位可以为 checkPoint 的高 32 位或者在此基础上±1,然后比较这三个方案哪个更接近 checkPoint 即可。
wrapping_integers.cc 实现为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
#include "wrapping_integers.hh"
using namespace std;
Wrap32 Wrap32::wrap( uint64_t n, Wrap32 zero_point )
{
// Your code here.
return Wrap32 { Wrap32(n) + zero_point.raw_value_ };
}
uint64_t Wrap32::unwrap( Wrap32 zero_point, uint64_t checkpoint ) const
// 转换为从0开始的绝对编号
{
// Your code here.
// checkpoint = 前32位+left
// 与checkpoint最近的可能有两个数(分布在checkpoint一左一右) 其中一个必定是 前32位+offset
// 如果offset < left 那么另一个必定比checkpoint大 等于前32位+zero_point+0x1 0000 0000
// 那么就要看checkpoint 更接近前32位+zero_point 还是前32位+zero_point+0x1 0000 0000
// 两边同减去前32位和zero_point 就是看 left-point 更接近0 还是0x 1 0000 0000
uint64_t offset = (raw_value_+0x1'0000'0000-zero_point.raw_value_)%0x1'0000'0000;
uint32_t left = checkpoint % 0x1'0000'0000;
uint64_t high32 = checkpoint - left;
// if( offset == left) {
// return high32+checkpoint;
// } else if ( offset < left){
if(offset < left){
if(left- offset <= 0x8000'0000) { // 更接近前32位+zero_point
return high32+ offset;
} else {
return high32+ offset +0x1'0000'0000;
}
} else {
// 同上,offset > left 那么另一个一定比check_point 小 等于前32位+zero_point-0x1 0000 0000
if( high32 == 0 || offset -left <= 0x8000'0000) { // 更接近前32位+zero_point
return high32+ offset;
} else {
return high32+ offset -0x1'0000'0000;
}
}
}
|
Implementing the TCP receiver#
接下来我们就可以实现 TCP receiver 了,实验过程中注意区分五个序号的概念,很容易搞混。另有几个关键逻辑值得一提:
- 如果收到 RST,需要将向内存字节流报告出错(很奇怪为啥
set_eroor 方法是 Reader 而不是 Writer 的);
- 收到 SYN 后更新
zero_point 和 ack_;
- 只有收到 SYN 后才能开始接收数据;
- 向包重组器发送数据后,根据内存中写入的数据量可以得到第一个待接收的数据的序号,进而更新
ack_;
- 如果数据全部接收完毕,
ack_ 更新时还要额外 +1(FIN 占了一个序号),接收完毕需要根据 writer.is_closed 来判断;
TCP_receiver 实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
#include "tcp_receiver.hh"
using namespace std;
void TCPReceiver::receive( TCPSenderMessage message )
{
// Your code here.
if(message.RST) {
reader().set_error();
return;
}
if(message.SYN){
zero_point_ = Wrap32(message.seqno);
ack_.emplace(message.seqno);
}
if(ack_.has_value()) {
const uint64_t check_point = writer().bytes_pushed()+1;
uint64_t first_index
= Wrap32( message.SYN ? message.seqno + 1 : message.seqno ).unwrap( zero_point_, check_point )-1;
reassembler_.insert( first_index, std::move(message.payload), message.FIN );
ack_ = ack_->wrap(writer().bytes_pushed()+1+writer().is_closed() , zero_point_);
}
}
TCPReceiverMessage TCPReceiver::send() const
{
// Your code here.
return {ack_,
static_cast<uint16_t>(min(reassembler_.writer().available_capacity(), static_cast<uint64_t>(UINT16_MAX))),
reader().has_error()};
}
|
运行结果为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
|
-- Building in 'Debug' mode.
-- Configuring done (0.3s)
-- Generating done (0.1s)
-- Build files have been written to: /home/zhouxin/projects/CS144/build
Test project /home/zhouxin/projects/CS144/build
Start 1: compile with bug-checkers
1/29 Test #1: compile with bug-checkers ........ Passed 19.75 sec
Start 3: byte_stream_basics
2/29 Test #3: byte_stream_basics ............... Passed 0.01 sec
Start 4: byte_stream_capacity
3/29 Test #4: byte_stream_capacity ............. Passed 0.01 sec
Start 5: byte_stream_one_write
4/29 Test #5: byte_stream_one_write ............ Passed 0.01 sec
Start 6: byte_stream_two_writes
5/29 Test #6: byte_stream_two_writes ........... Passed 0.01 sec
Start 7: byte_stream_many_writes
6/29 Test #7: byte_stream_many_writes .......... Passed 0.06 sec
Start 8: byte_stream_stress_test
7/29 Test #8: byte_stream_stress_test .......... Passed 0.05 sec
Start 9: reassembler_single
8/29 Test #9: reassembler_single ............... Passed 0.01 sec
Start 10: reassembler_cap
9/29 Test #10: reassembler_cap .................. Passed 0.01 sec
Start 11: reassembler_seq
10/29 Test #11: reassembler_seq .................. Passed 0.01 sec
Start 12: reassembler_dup
11/29 Test #12: reassembler_dup .................. Passed 0.05 sec
Start 13: reassembler_holes
12/29 Test #13: reassembler_holes ................ Passed 0.01 sec
Start 14: reassembler_overlapping
13/29 Test #14: reassembler_overlapping .......... Passed 0.01 sec
Start 15: reassembler_win
14/29 Test #15: reassembler_win .................. Passed 0.15 sec
Start 16: wrapping_integers_cmp
15/29 Test #16: wrapping_integers_cmp ............ Passed 0.04 sec
Start 17: wrapping_integers_wrap
16/29 Test #17: wrapping_integers_wrap ........... Passed 0.01 sec
Start 18: wrapping_integers_unwrap
17/29 Test #18: wrapping_integers_unwrap ......... Passed 0.01 sec
Start 19: wrapping_integers_roundtrip
18/29 Test #19: wrapping_integers_roundtrip ...... Passed 0.56 sec
Start 20: wrapping_integers_extra
19/29 Test #20: wrapping_integers_extra .......... Passed 0.12 sec
Start 21: recv_connect
20/29 Test #21: recv_connect ..................... Passed 0.01 sec
Start 22: recv_transmit
21/29 Test #22: recv_transmit .................... Passed 0.12 sec
Start 23: recv_window
22/29 Test #23: recv_window ...................... Passed 0.01 sec
Start 24: recv_reorder
23/29 Test #24: recv_reorder ..................... Passed 0.04 sec
Start 25: recv_reorder_more
24/29 Test #25: recv_reorder_more ................ Passed 0.36 sec
Start 26: recv_close
25/29 Test #26: recv_close ....................... Passed 0.04 sec
Start 27: recv_special
26/29 Test #27: recv_special ..................... Passed 0.04 sec
Start 37: compile with optimization
27/29 Test #37: compile with optimization ........ Passed 1.93 sec
Start 38: byte_stream_speed_test
ByteStream throughput: 18.15 Gbit/s
28/29 Test #38: byte_stream_speed_test ........... Passed 0.06 sec
Start 39: reassembler_speed_test
Reassembler throughput: 9.03 Gbit/s
29/29 Test #39: reassembler_speed_test ........... Passed 0.11 sec
100% tests passed, 0 tests failed out of 29
Total Test time (real) = 23.60 sec
Built target check2
|
Lab 3#
Lab 3 要求实现一个 sender,这里实现了 TCP 的超时重传和拥塞控制算法。需要实现如下几个方法:
uint64_t TCPSender::sequence_numbers_in_flight() const:返回待确认的字节数uint64_t TCPSender::consecutive_retransmissions() const:返回连续重传报文的数目void TCPSender::push( const TransmitFunction& transmit ):从内存字节流中读取待发送数据,尽可能填满接收窗口TCPSenderMessage TCPSender::make_empty_message() const:产生一条不占用序号的空消息void TCPSender::receive( const TCPReceiverMessage& msg ):接收来自接受者的确认消息,维护接收窗口的大小void TCPSender::tick( uint64_t ms_since_last_tick, const TransmitFunction& transmit ):根据外部传入的时间判断是否需要重传和进行拥塞控制
在实现 push 的过程中,有如下值得注意的地方:
- 使用字段
current_seq_ 记录当前需要发送的序号,第一次建立连接(current_seq_=0)时,需要将 SYN 字段设置为 true;
push 方法仅用于首次发送消息,发送过的所有消息都保存在一个队列中,等待重传或者确认。在发送过 FIN 报文后,push 方法不应再发送任何消息,报文重传由 tick 方法负责;- 原文提到,若接收窗口为 0,则在发送报文时应该视为 1;
push 方法应该存在一个循环,用于处理接收窗口很大,待发送数据超过单个 TCP 包上限,需要发送多个包的情况;
剩余部分跟着文档逻辑写,面向测试用例 debug。我在 tcp_sender.hh 中使用了如下成员变量:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
ByteStream input_;
Wrap32 isn_;
uint64_t initial_RTO_ms_;
uint64_t current_time_;
uint64_t ack_;
uint64_t in_flight_cnt_;
uint64_t expire_time_;
uint64_t retrans_cnt_;
uint64_t window_size_;
uint64_t rto_;
uint64_t current_seq_;
Wrap32 zero_point_;
std::deque<TCPSenderMessage> outstanding_msg_;
bool is_fin_sent;
|
tcp_sender.cc 各函数实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
|
#include "tcp_sender.hh"
#include "tcp_config.hh"
using namespace std;
uint64_t TCPSender::sequence_numbers_in_flight() const
{
// Your code here.
return in_flight_cnt_;
}
uint64_t TCPSender::consecutive_retransmissions() const
{
// Your code here.
return retrans_cnt_;
}
void TCPSender::push( const TransmitFunction& transmit )
{
// Your code here.
bool window_zero = window_size_ == 0;
uint64_t available_window
= ( window_size_ + window_zero ) < in_flight_cnt_ ? 0 : window_size_ + window_zero - in_flight_cnt_;
do {
// 先考虑SYN和RST,FIN要等到把buffer读空才能判断
if ( is_fin_sent )
return;
uint64_t pay_load_size = min( reader().bytes_buffered(), TCPConfig::MAX_PAYLOAD_SIZE );
uint64_t seq_size = min( available_window, pay_load_size + ( current_seq_ == 0 ) );
pay_load_size = seq_size;
TCPSenderMessage msg = TCPSenderMessage();
if ( current_seq_ == 0 ) {
msg.SYN = true;
pay_load_size--;
}
if ( reader().has_error() ) {
msg.RST = true;
}
while ( msg.payload.size() < pay_load_size ) {
string_view front_view = reader().peek();
uint64_t bytes_to_read = min( front_view.size(), pay_load_size - msg.payload.size() );
msg.payload += front_view.substr( 0, bytes_to_read );
input_.reader().pop( bytes_to_read );
}
if ( reader().is_finished() && seq_size < available_window ) {
msg.FIN = true;
seq_size++;
is_fin_sent = true;
}
if ( msg.sequence_length() == 0 )
return;
msg.seqno = Wrap32::wrap( current_seq_, zero_point_ );
current_seq_ += msg.sequence_length();
in_flight_cnt_ += msg.sequence_length();
outstanding_msg_.push_back( msg );
transmit( msg );
if ( expire_time_ == UINT64_MAX )
expire_time_ = current_time_ + rto_;
available_window
= ( window_size_ + window_zero ) < in_flight_cnt_ ? 0 : window_size_ + window_zero - in_flight_cnt_;
} while ( reader().bytes_buffered() != 0 && available_window != 0 );
}
TCPSenderMessage TCPSender::make_empty_message() const
{
// Your code here.
return { Wrap32::wrap( current_seq_, zero_point_ ), false, string(), false, reader().has_error() };
}
void TCPSender::receive( const TCPReceiverMessage& msg )
{
// Your code here.
if ( msg.ackno.has_value() ) {
uint64_t ack_from_recv = unwarp( msg.ackno.value() );
if ( ack_from_recv > ack_ && ack_from_recv <= current_seq_ ) {
ack_ = ack_from_recv;
rto_ = initial_RTO_ms_;
expire_time_ = current_time_ + rto_;
retrans_cnt_ = 0;
while ( !outstanding_msg_.empty() ) {
auto& front_msg = outstanding_msg_.front();
if ( unwarp( front_msg.seqno ) + front_msg.sequence_length() > ack_ )
break;
in_flight_cnt_ -= front_msg.sequence_length();
outstanding_msg_.pop_front();
}
if ( outstanding_msg_.empty() ) {
expire_time_ = UINT64_MAX;
}
}
}
window_size_ = msg.window_size;
if ( msg.RST )
writer().set_error();
}
void TCPSender::tick( uint64_t ms_since_last_tick, const TransmitFunction& transmit )
{
// Your code here.
current_time_ += ms_since_last_tick;
if ( expire_time_ != 0 && current_time_ >= expire_time_ ) {
transmit( outstanding_msg_.front() );
// auto msg = outstanding_msg_.front();
// outstanding_msg_.pop_front();
// outstanding_msg_.push_back(msg);
// transmit(msg);
if ( window_size_ != 0 ) {
retrans_cnt_++;
rto_ *= 2;
}
expire_time_ = current_time_ + rto_;
}
}
uint64_t TCPSender::unwarp( const Wrap32& seq )
{
return seq.unwrap( zero_point_, ack_ );
}
|
运行结果为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
|
-- Building in 'Debug' mode.
-- Configuring done (0.3s)
-- Generating done (0.3s)
-- Build files have been written to: /home/zhouxin/projects/CS144/build
Test project /home/zhouxin/projects/CS144/build
Start 1: compile with bug-checkers
1/36 Test #1: compile with bug-checkers ........ Passed 40.66 sec
Start 3: byte_stream_basics
2/36 Test #3: byte_stream_basics ............... Passed 0.02 sec
Start 4: byte_stream_capacity
3/36 Test #4: byte_stream_capacity ............. Passed 0.01 sec
Start 5: byte_stream_one_write
4/36 Test #5: byte_stream_one_write ............ Passed 0.01 sec
Start 6: byte_stream_two_writes
5/36 Test #6: byte_stream_two_writes ........... Passed 0.01 sec
Start 7: byte_stream_many_writes
6/36 Test #7: byte_stream_many_writes .......... Passed 0.05 sec
Start 8: byte_stream_stress_test
7/36 Test #8: byte_stream_stress_test .......... Passed 0.05 sec
Start 9: reassembler_single
8/36 Test #9: reassembler_single ............... Passed 0.01 sec
Start 10: reassembler_cap
9/36 Test #10: reassembler_cap .................. Passed 0.01 sec
Start 11: reassembler_seq
10/36 Test #11: reassembler_seq .................. Passed 0.01 sec
Start 12: reassembler_dup
11/36 Test #12: reassembler_dup .................. Passed 0.05 sec
Start 13: reassembler_holes
12/36 Test #13: reassembler_holes ................ Passed 0.01 sec
Start 14: reassembler_overlapping
13/36 Test #14: reassembler_overlapping .......... Passed 0.01 sec
Start 15: reassembler_win
14/36 Test #15: reassembler_win .................. Passed 0.17 sec
Start 16: wrapping_integers_cmp
15/36 Test #16: wrapping_integers_cmp ............ Passed 0.04 sec
Start 17: wrapping_integers_wrap
16/36 Test #17: wrapping_integers_wrap ........... Passed 0.01 sec
Start 18: wrapping_integers_unwrap
17/36 Test #18: wrapping_integers_unwrap ......... Passed 0.01 sec
Start 19: wrapping_integers_roundtrip
18/36 Test #19: wrapping_integers_roundtrip ...... Passed 0.55 sec
Start 20: wrapping_integers_extra
19/36 Test #20: wrapping_integers_extra .......... Passed 0.12 sec
Start 21: recv_connect
20/36 Test #21: recv_connect ..................... Passed 0.01 sec
Start 22: recv_transmit
21/36 Test #22: recv_transmit .................... Passed 0.13 sec
Start 23: recv_window
22/36 Test #23: recv_window ...................... Passed 0.01 sec
Start 24: recv_reorder
23/36 Test #24: recv_reorder ..................... Passed 0.04 sec
Start 25: recv_reorder_more
24/36 Test #25: recv_reorder_more ................ Passed 0.39 sec
Start 26: recv_close
25/36 Test #26: recv_close ....................... Passed 0.04 sec
Start 27: recv_special
26/36 Test #27: recv_special ..................... Passed 0.04 sec
Start 28: send_connect
27/36 Test #28: send_connect ..................... Passed 0.04 sec
Start 29: send_transmit
28/36 Test #29: send_transmit .................... Passed 0.18 sec
Start 30: send_retx
29/36 Test #30: send_retx ........................ Passed 0.04 sec
Start 31: send_window
30/36 Test #31: send_window ...................... Passed 0.07 sec
Start 32: send_ack
31/36 Test #32: send_ack ......................... Passed 0.04 sec
Start 33: send_close
32/36 Test #33: send_close ....................... Passed 0.04 sec
Start 34: send_extra
33/36 Test #34: send_extra ....................... Passed 0.05 sec
Start 37: compile with optimization
34/36 Test #37: compile with optimization ........ Passed 2.29 sec
Start 38: byte_stream_speed_test
ByteStream throughput: 19.14 Gbit/s
35/36 Test #38: byte_stream_speed_test ........... Passed 0.06 sec
Start 39: reassembler_speed_test
Reassembler throughput: 8.26 Gbit/s
36/36 Test #39: reassembler_speed_test ........... Passed 0.12 sec
100% tests passed, 0 tests failed out of 36
Total Test time (real) = 45.37 sec
Built target check3
|
Lab 4#
lab 4 的任务是使用我们之前写的 TCP 模块与外网进行通信,如果前面实现的都没问题,那么这里是不需要写代码的。按照文档指示执行,顺利通过测试,运行结果为:
1
2
3
4
5
|
Test project /home/zhouxin/projects/CS144/build
Start 1: compile with bug-checkers
1/2 Test #1: compile with bug-checkers ........ Passed 0.11 sec
Start 2: t_webget
2/2 Test #2: t_webget ......................... Passed 1.03 sec
|
Lab 5#
lab 5 实现了 ARP 协议,负责将 IP 地址转换为 MAC 地址,并发送来自传输层的报文。有如下细节值得注意:
- 内存中需要维护一张 arp 表,每一个表项只有 30 秒的有效时间
- 相同目标 ip 的 arp 请求间隔为 5 秒钟
- 发送数据时,arp 表中没有对应记录,则先发出 arp 请求
- 收到 arp 回复报文后,需要将等待该记录的所有报文全部发出
实现过程中,我新增了三个数据结构:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
// 当前时间
size_t current_time_;
// 保存arp表
std::unordered_map<uint32_t , std::pair<EthernetAddress, size_t>> arp_table_;
// 等待arp请求的信号量队列
std::unordered_map<uint32_t ,std::pair<std::queue<EthernetFrame>, std::optional<size_t>>> frame_queue_;
|
arp 表每一条的有效时间只有 30 秒,因此每一行都要记录 ip 地址对应的 mac 地址和过期时间;在发送报文的方法中,如果目标 ip 的 mac 地址还不知道,则先把数据报插入到等待队列中,等待收到 arp 回复报文再发送报文(本质上是使用信号量实现同步关系);此外,还要记录目标 ip 上次 arp 请求的时间,防止对同一个 ip 请求过于频繁。
实现 send_datagram 的逻辑为:首先填写数据帧中除目标 MAC 之外的字段,然后查询 arp 表,如果存在目标 ip 的有效条目,则填写 MAC 并发送;否则将待发送帧放入目标 ip 对应的队列,并发出 arp 请求。
实现 recv_frame 的逻辑为:首先根据 MAC 字段判断是否是发给自己的数据帧,只处理目标为自己或者广播地址的帧。然后根据类型字段对有效载荷解析,如果是 ip 包直接把解析包交付给上层队列;如果是 arp 包则根据协议头将更新 arp 表,如果收到的是 arp 请求报文,则构造 arp 回复报文回复自己的 mac,如果收到的是 arp 回复报文,则查看对应 ip 的待发送消息的队列,发送其中所有的消息。
详细实现的代码为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
|
#include <iostream>
#include "arp_message.hh"
#include "exception.hh"
#include "network_interface.hh"
using namespace std;
//! \param[in] ethernet_address Ethernet (what ARP calls "hardware") address of the interface
//! \param[in] ip_address IP (what ARP calls "protocol") address of the interface
NetworkInterface::NetworkInterface( string_view name,
shared_ptr<OutputPort> port,
const EthernetAddress& ethernet_address,
const Address& ip_address )
: name_( name )
, port_( notnull( "OutputPort", move( port ) ) )
, ethernet_address_( ethernet_address )
, ip_address_( ip_address )
, current_time_(0)
, arp_table_()
, frame_queue_()
{
cerr << "DEBUG: Network interface has Ethernet address " << to_string( ethernet_address ) << " and IP address "
<< ip_address.ip() << "\n";
}
//! \param[in] dgram the IPv4 datagram to be sent
//! \param[in] next_hop the IP address of the interface to send it to (typically a router or default gateway, but
//! may also be another host if directly connected to the same network as the destination) Note: the Address type
//! can be converted to a uint32_t (raw 32-bit IP address) by using the Address::ipv4_numeric() method.
void NetworkInterface::send_datagram( const InternetDatagram& dgram, const Address& next_hop )
{
// Your code here.
EthernetFrame messsage = EthernetFrame();
const uint32_t target_ip = next_hop.ipv4_numeric();
messsage.header.src = ethernet_address_;
messsage.header.type = EthernetHeader::TYPE_IPv4;
messsage.payload = serialize(dgram);
if(!arp_table_.contains(target_ip) || arp_table_[target_ip].second < current_time_){
frame_queue_[target_ip].first.push(std::move(messsage));
EthernetFrame arp_request_frame;
send_arp_request( target_ip, arp_request_frame );
return;
} else {
messsage.header.dst = arp_table_[target_ip].first;
transmit(messsage);
}
}
void NetworkInterface::send_arp_request( const uint32_t target_ip, EthernetFrame& arp_request_frame )
{
if(frame_queue_.contains(target_ip) && frame_queue_[target_ip].second.has_value()
&& frame_queue_[target_ip].second >= current_time_)
return;
arp_request_frame.header.type = EthernetHeader::TYPE_ARP;
arp_request_frame.header.dst = ETHERNET_BROADCAST;
arp_request_frame.header.src = ethernet_address_;
ARPMessage arp_request_message = ARPMessage();
arp_request_message.sender_ethernet_address = ethernet_address_;
arp_request_message.sender_ip_address = ip_address_.ipv4_numeric();
arp_request_message.opcode = ARPMessage::OPCODE_REQUEST;
arp_request_message.target_ip_address = target_ip;
// arp_request_message.target_ethernet_address = ETHERNET_BROADCAST;
arp_request_frame.payload = serialize(arp_request_message);
transmit(arp_request_frame);
frame_queue_[target_ip].second = current_time_ + 5000;
}
//! \param[in] frame the incoming Ethernet frame
void NetworkInterface::recv_frame( const EthernetFrame& frame )
{
// Your code here.
if(frame.header.dst == ethernet_address_ || frame.header.dst == ETHERNET_BROADCAST){
if(frame.header.type == EthernetHeader::TYPE_ARP){
ARPMessage message = ARPMessage();
if(parse(message, frame.payload) && message.target_ip_address == ip_address_.ipv4_numeric()) {
arp_table_[message.sender_ip_address] = make_pair(message.sender_ethernet_address, current_time_+30000);
if(message.opcode == ARPMessage::OPCODE_REQUEST){
EthernetFrame response = EthernetFrame();
make_arp_response( message, response );
transmit(response);
} else {
// 收到arp回复之后看对应ip有无待发送的消息
queue<EthernetFrame>& ip_queue = frame_queue_[message.sender_ip_address].first;
while (!ip_queue.empty()){
ip_queue.front().header.dst = message.sender_ethernet_address;
transmit(ip_queue.front());
ip_queue.pop();
}
}
}
} else if(frame.header.type == EthernetHeader::TYPE_IPv4){
InternetDatagram message = InternetDatagram();
if(parse(message, frame.payload)){
datagrams_received_.emplace(std::move(message));
}
}
}
}
void NetworkInterface::make_arp_response( const ARPMessage& message, EthernetFrame& response ) const
{
EthernetHeader& header = response.header;
header.dst = message.sender_ethernet_address;
header.src = ethernet_address_;
header.type = EthernetHeader::TYPE_ARP;
ARPMessage arp_response_message = ARPMessage();
arp_response_message.opcode = ARPMessage::OPCODE_REPLY;
arp_response_message.sender_ethernet_address = ethernet_address_;
arp_response_message.sender_ip_address = ip_address_.ipv4_numeric();
arp_response_message.target_ethernet_address = message.sender_ethernet_address;
arp_response_message.target_ip_address = message.sender_ip_address;
response.payload = serialize(arp_response_message);
return;
}
//! \param[in] ms_since_last_tick the number of milliseconds since the last call to this method
void NetworkInterface::tick( const size_t ms_since_last_tick )
{
// Your code here.
current_time_ += ms_since_last_tick;
}
|
运行结果为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
Test project /home/zhouxin/projects/CS144/build
Start 1: compile with bug-checkers
1/2 Test #1: compile with bug-checkers ........ Passed 8.79 sec
Start 35: net_interface
2/2 Test #35: net_interface .................... Passed 0.01 sec
100% tests passed, 0 tests failed out of 2
Total Test time (real) = 8.80 sec
Built target check5
|
Lab 6#
在 lab 6,我们将实现路由转发。具体来说,需要在内存中维护一张路由表,并根据路由表做最长匹配,进而实现网络层的转发。
路由表比较理想的数据结构是前缀树,但建树的过程难免要用到智能指针,遂作罢。且文档中也说 O(n) 复杂度也是可接受的,因此我最终选择 vector 来保存路由表。路由表中,我没有保存前缀长度,而是将前缀长度转换为子网掩码,以方便后续匹配。
匹配使用与运算进行,当且仅当 ip & mask == prefix 时,说明 ip 是匹配 prefix 的。一个 ip 可能匹配多个 prefix,可以根据 mask 的大小找到最长匹配。
找到最长匹配后,如果路由表项中还有下一跳,则转发到下一跳 ip;如果没有下一跳,说明直接交付给指定 ip 即可,即转发到目标 ip。
route() 的实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
void Router::route()
{
// Your code here.
for( auto& interface: _interfaces){
auto& data_queue = interface->datagrams_received();
while(!data_queue.empty()){
InternetDatagram &data = data_queue.front();
if(data.header.ttl == 0 || data.header.ttl == 1) {
data_queue.pop();
continue;
}
data.header.ttl -= 1;
data.header.compute_checksum();
uint32_t ip = data.header.dst;
optional<routing_item> best_match;
for(uint32_t i=0; i<routing_table_.size(); i++){
auto& item = routing_table_[i];
if(item.route_prefix_ == (ip & item.mask_)){
if(!best_match.has_value() || best_match->mask_ < item.mask_){
best_match = item;
}
}
}
if(best_match.has_value()){
auto &next_interface = _interfaces.at(best_match->interface_num_);
if(best_match->next_hop_.has_value()){
next_interface->send_datagram(data, best_match->next_hop_.value());
} else {
next_interface->send_datagram(data, Address::from_ipv4_numeric(data.header.dst));
}
}
data_queue.pop();
}
}
}
|
运行结果为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
Test project /home/zhouxin/projects/CS144/build
Start 1: compile with bug-checkers
1/3 Test #1: compile with bug-checkers ........ Passed 9.56 sec
Start 35: net_interface
2/3 Test #35: net_interface .................... Passed 0.02 sec
Start 36: router
3/3 Test #36: router ........................... Passed 0.01 sec
100% tests passed, 0 tests failed out of 3
|


